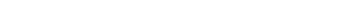The release of ChatGPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) on November 30, 2022, has been a global phenomenon. From a standstill, the software has grown faster than Instagram, Facebook, or Twitter.1 It took only five days for ChatGPT to hit 1 million users. By April 2023, the site had been visited over 1.8 billion times.
Discussions around the watercooler hint at the tool’s ability to automate, simplify, or replace the tasks many common white-collar workers perform, including researching, writing, analyzing, summarizing, and problem-solving. And while research is in its early stages, a study (admittedly, perhaps biased because most of the researchers work for the company that released ChatGPT) has concluded that there will be significant disruption to the white-collar workforce in the immediate future:
Our findings indicate that approximately 80% of the U.S. workforce could have at least 10% of their work tasks affected by the introduction of GPTs, while around 19% of workers may see at least 50% of their tasks impacted. The influence spans all wage levels, with higher-income jobs potentially facing greater exposure. Notably, the impact is not limited to industries with higher recent productivity growth.2
Another report by Goldman Sachs cites that generative artificial intelligence (AI) will expose and/or replace up to 300 million jobs3 over the coming decades.
Companies always need to be scanning for technologies that could upend their business model and be aware of potential innovations that might disrupt their business and embolden new entrants. By identifying and embracing the new technology first, companies can keep or improve their market position, customer centricity, and profitability.
If you or your company were “surprised” by ChatGPT and other generative AI, are worried about what it (they) can do, and wonder what you should do next, keep reading. In this article, we will explain generative AI (including solutions like ChatGPT), its underlying capabilities, and some relevant use cases. Once we’ve established a baseline, we’ll outline what you should be doing now to transform your business and incrementally improve many, if not most, of your business functions.
An Overview of Generative AI
So, how was a tool like ChatGPT released seemingly overnight? It wasn’t. OpenAI, a San Francisco-based research lab founded in 2015, introduced an earlier version of the software, ChatGPT 3, in 2020. And what became an overnight sensation resulted from decades of hard work. Since the inception of artificial intelligence in the 1940s, countless researchers have been building the foundation to get us to where we are today. ChatGPT is one of many (perhaps hundreds) of AI and other technology-based disruptions that will be released at an accelerating pace.
But what is ChatGPT exactly? ChatGPT is a software tool in a class loosely called Generative AI. generative AI, also known as deep learning, is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables machines to learn from data and generate new content, such as images, music, and text. While traditional AI systems are designed to perform specific tasks, such as recognizing objects or analyzing data, generative AI can create new content for various applications.
To date, the term “new” needs to be taken with a grain of salt, as AI can only replicate patterns that it sees in the large volumes of data used to train it. Thus, it isn’t so much creating something “new” as applying patterns from one area of data to another. It looks new but, in reality, is pattern recognition and replication. One could argue, however, that the human mind often creates something “new” in the same way.
Generative AI Democratizing Technology
“We’re a technology company” is a common phrase used by many business leaders such as JP Morgan’s Jamie Dimon.4 Because technology provides ample benefits and competitive advantages to organizations, leaders often brand themselves as techno-centrist organizations. However, in truth, many are not — they’re merely trying to leverage technology to enhance their core competencies. For a bank, this might be risk management. For retailers, it could be marketing and supply chain management. In most cases, the companies are focusing on technology as the end rather than the means for building and evolving their businesses. Organizations identified an opportunity to build a moat using technology, which in many cases led organizations astray. Acquiring a shiny startup and overhiring or overpaying technology talent are both examples witnessed.
With AI, however, organizations can now leverage technology more effectively and efficiently to drive outcomes and focus on what matters most for their businesses.
This is because AI significantly reduces the software development life cycle (SDLC) cost and allows organizations to rapidly develop, deploy, and integrate their existing technology systems. Over the past 30 years, we’ve seen information technology and bespoke software as a service (SaaS) provide operational advantages to organizations. Many organizations, big and small, have struggled to capitalize on the advantage technology can provide, as they lacked the technical talent and willingness to invest in transformative technologies.
However, organizations are now enabled to transform their businesses by harnessing the power of AI to develop customized and integrated solutions at a lower cost. Generative AI allows organizations to democratize technology by building bespoke solutions and customizing existing systems to best meet the organization’s needs. By coupling existing developers and technical talent with AI solutions, the overall software development life cycle can be reduced significantly. AI solutions achieve this in several key ways:
- Improving code quality by identifying bugs more quickly and earlier in the development life cycle; AI can also automate testing processes to mitigate the time to ship products.
- Automating code generation by eliminating the need for developers to spend time conducting simple and basic development tasks.
- Enabling speed to integrate and “modernize” existing technology products by reducing the time to write APIs and translate existing code to different coding languages.
Reducing the software development life cycle not only allows organizations to build and customize existing software to best suit their needs, but it ultimately reduces the cost of maintenance, increases the value of technology, and eliminates technology bottlenecks.
As organizations evolve their existing technology stacks and usage, they will have the ability to refocus their attention on the factors that determine the success of their business.
How Generative AI Will Change Common Business Functions
There are many benefits to using generative AI, and an imaginative mind can combine them in novel ways to impact their company’s core value proposition. Following are 12 examples of how AI will change common business functions and processes. It is important to consider how these changes will impact your organization and prepare effectively to embrace forthcoming disruption. Any one of these applications can be applied to provide incremental improvement to the business. Every business should be engaged in that analysis on an ongoing basis. At the same time, however, businesses should also be thinking about how these applications work together and in groups to potentially disrupt value creation more broadly and threaten legacy business models.

How AI will change common business functions and processes
1.
Audit And Compliance
Transform existing audit and compliance processes by using AI to conduct manual reporting and necessary risk analysis.
2.
Content Generation
Create content for marketing, advertising, and social media, saving time and resources. This allows companies to do more with less.
3.
Customer Segmentation and Personalization
Analyze customer data and create personalized recommendations, offers, or products tailored to individual needs. This improves customer engagement and retention.
4.
Customer Service
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants provide more accurate, personalized, and faster support, thus improving customer experience.
5.
Data Analysis and Predictive Analytics
Leverage big data using automated AI-powered algorithms and machine learning models to identify trends and predict future trends.
6.
Data Analysis and Decision-making
AI processes and analyzes vast amounts of data to identify patterns, trends, and opportunities, thus enabling data-driven decision-making and strategy development.
7.
Dynamic Pricing
Analyze market conditions, customer behavior, and other factors to dynamically adjust pricing, thereby maximizing revenue and staying competitive.
8.
Efficiency
Any area of business where logic and data applications can be accelerated, simplified, and improved with AI, particularly in pattern detection and process acceleration.
9.
Product Optimization
Design and prototype new products or features based on customer preferences, market trends, or other relevant factors. This enables faster and more efficient innovation.
10.
Process Optimization
Analyze and optimize business processes, identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for automation. This helps reduce costs and improve operational efficiency.
11.
Software Development
Reduce the software development life cycle by using Generative AI to produce/edit lines of code and build functional working products.
12.
Supply Chain Management
Optimize inventory levels, demand forecasting, and logistics, leading to cost reductions and improved efficiency throughout the supply chain.
Generative AI, also known as deep learning, is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables machines to learn from data and generate new content, such as images, music, and text.
AI Opportunity Assessment
As we discussed in a previous Jabian Journal article on business model disruption,5 most businesses focus on convergent activities. With its customer base, key products, and method of competition clear, the business focuses on optimization and squeezing out every nickel of profit. To assess technologies and their ability to “upset the apple cart,” it’s important to charter a divergent team that thinks creatively about using advanced technologies to provide value over and above the business’s existing operating model. This team should focus on the customer problem and customer value, without considering organizational politics, jobs, shareholders, and other factors that traditionally constrain decision-making.
“The rise of generative AI should not be a cause for anxiety but rather an invitation for businesses to embrace change, reinvent themselves, and turn that new technology into a strategic advantage.”
Any organization needs to understand areas of their business where they can leverage AI and assess the size of that opportunity by using the AI Assessment Framework. From there, organizations can identify ways to leverage technology to best achieve and provide value and achieve their missions. We’ve outlined multiple use cases above as a starting point, but you can identify more specific use cases relevant to your organization by gathering a team of senior leaders. Then use the framework above to assess and develop an implementation roadmap based on your existing priorities and capacity.
Immediate Action
Opportunities that are impactful either for a business model or profitability reasons and are easy to execute must be implemented quickly, as low barriers ensure your competitors can easily follow suit. To do otherwise risks your products becoming less competitive and your profit margins shrinking compared to the competition.
Lock In/Protect
Any opportunity that impacts your primary business model/value proposition and can be locked in and protected — or that is difficult for your competitors to achieve — must be pursued with gusto. Form a divergent team, give them a charter and resources, and have at it.3 If you are in aluminum manufacturing, for example, your divergent teams should focus on the identification of new alloys and improving manufacturing efficiency, quality, safety, and cost.
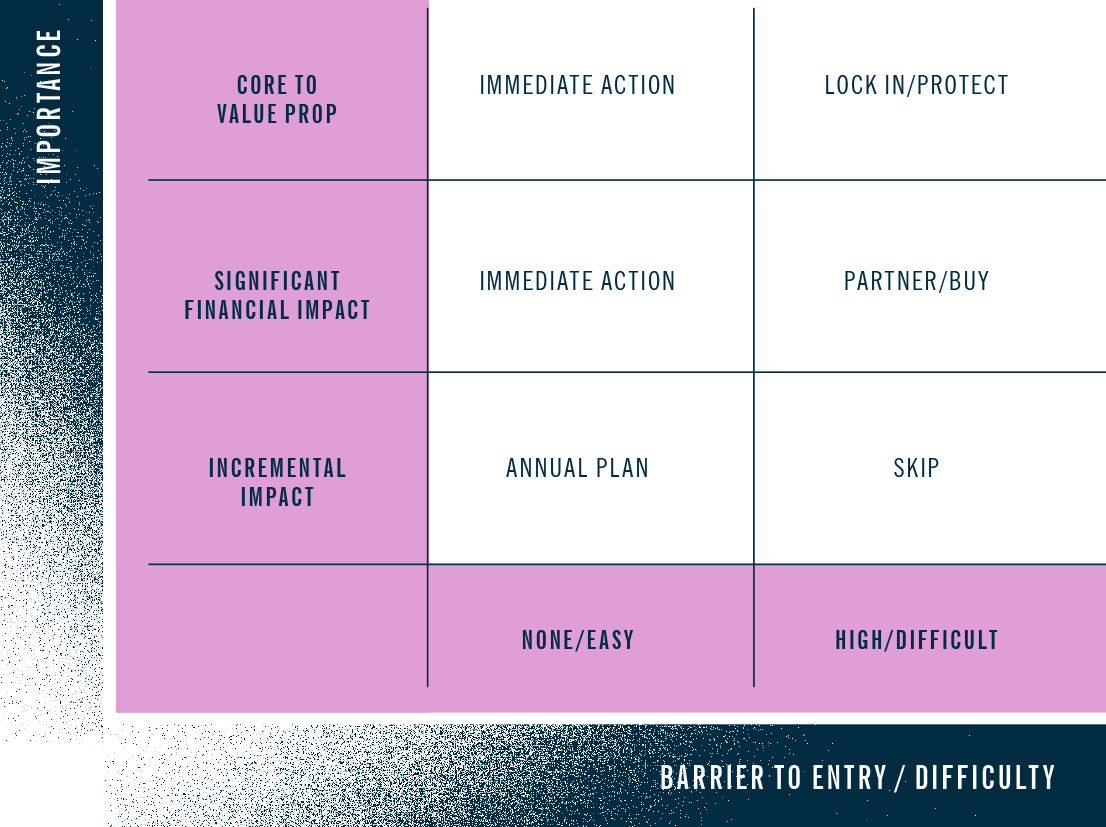
Partner/Buy
If something is identified that will improve profits significantly but is non-core to your business, consider partnering with someone for whom the solution is core to their business. You have scarce resources, especially in areas such as analytics and AI, and you want those scarce resources focused on your core value proposition. Let someone else drive your non-core expenses lower, or your non-core revenue higher.
An example of this might be back office or call center operations. Important, and expensive, but if it’s not core to your value proposition, partner or buy a solution. Do not focus your scarce talent on it. Rather, wait for your enterprise resource planning (ERP) vendor to incorporate generative AI into your back office. Or wait for your customer relationship management (CRM) vendor to incorporate generative AI into the request for proposal (RFP) creation.
Annual Plan
Ideas that have an incremental aspect to their improvement but are relatively easy to execute should be folded into the company’s annual planning.
Skip
Difficult-to-implement ideas with limited to incremental improvement should be put on the back burner and only considered when (if ever) all other ideas have been implemented.
In Conclusion
Gone are the days when technology represents an uncrossable moat for organizations. The rise of generative AI should not be a cause for anxiety but rather an invitation for businesses to embrace change, reinvent themselves, and turn that new technology into a strategic advantage. The question is no longer about whether to adopt AI, but rather how quickly and strategically it can be harnessed. Companies that recognize this, adapt, and evolve accordingly, will not only survive but also thrive in our AI-driven future. The future belongs to them, and that future is now.
- https://explodingtopics.com/blog/chatgpt-users
- GPTs are GPTs: An Early Look at the Labor Market Impact Potential of Large Language Models https://digitaleconomy.stanford.edu/publications/gpts-are-gpts-an-early-look-at-the-labor-market-impact-potential-of-large-language-models/ (Note, 3 of the 4 researchers work for OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT. The 4th researcher works for the University of Pennsylvania.)
- Hatzius, J., Briggs, J., Kodnani, D., & Pierdomenico, G. (2023, March 26). The Potentially Large Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Economic Growth. Goldman Sachs Economic Research. https://www.key4biz.it/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Global-Economics-Analyst_-The-Potentially-Large-Effects-of-Artificial-Intelligence-on-Economic-Growth-Briggs_Kodnani.pdf
- Dimon, J. (2015). Letter to Shareholders. JPMorgan Chase & Co. Retrieved from https://www.jpmorganchase.com/content/dam/jpmc/jpmorgan-chase-and-co/investor-relations/documents/2015-annualreport.pdf
- “It’s Officially Time To Self-Disrupt”, Jabian Journal, Fall 2019 https://journal.jabian.com/its-officially-time-to-self-disrupt/